广度优先搜索(Breadth-first search)
广度优先搜索简称广搜或者BFS,BFS和DFS一样是一种图算法,dijkstra算法和最小生成树prim算法也有用到BFS的思想。通俗一点讲BFS就是暴力的辐射状一样搜索每一种可能出现的情况来找到答案。
下面来我们还是先看个图
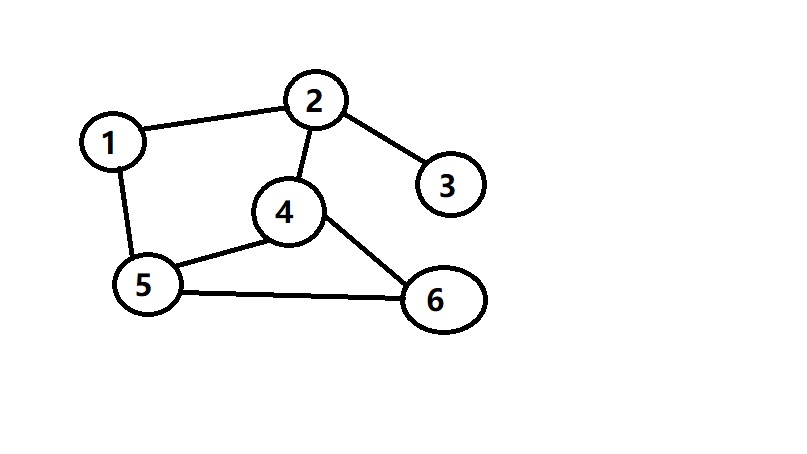
让我们从1开始,同时我们用队列来模拟(因为大部分BFS程序都是拿队列来实现的),
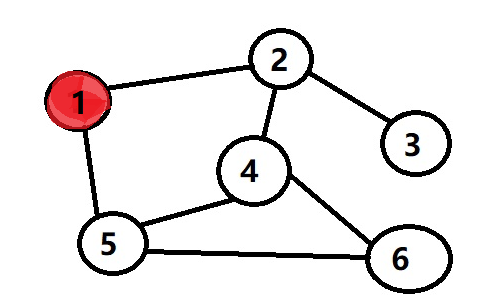
选到1我们就把1从队列中拿出去,然后把1的邻接点2和5放入队列中。
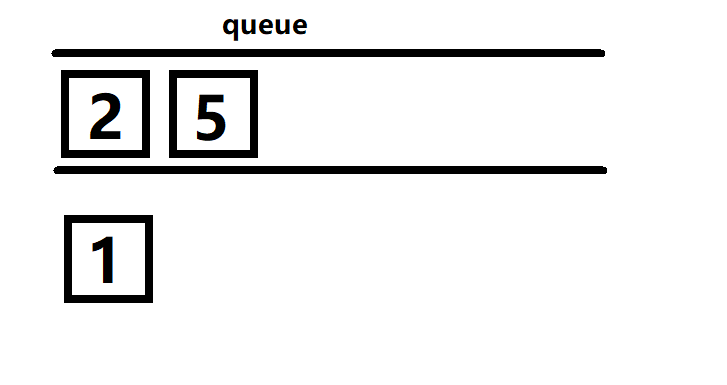
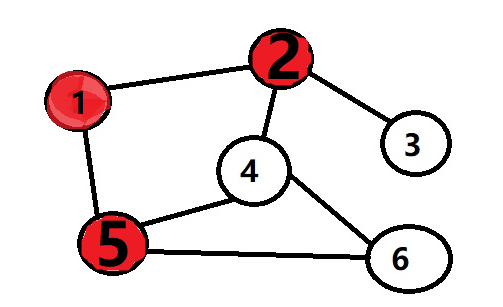
然后把队列中的2拿出来,又把2的邻接点3和4放入到队列中。
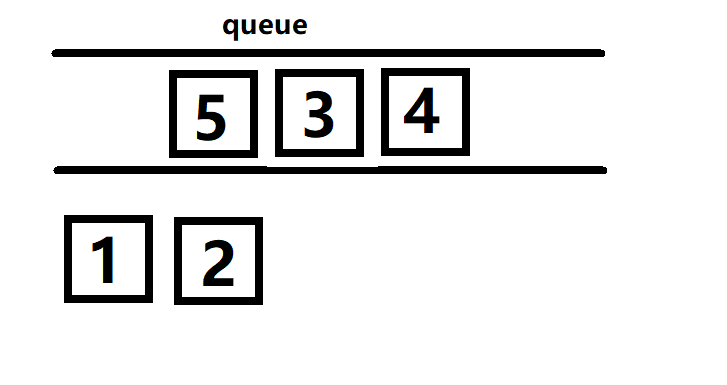
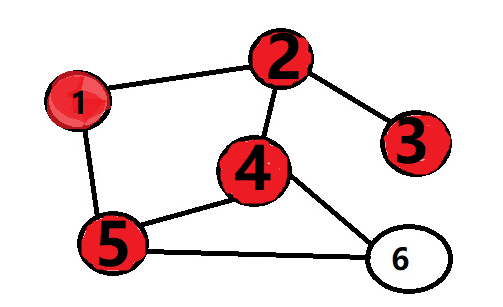
然后把队列中的5拿出来,把5的邻接点6放进去。
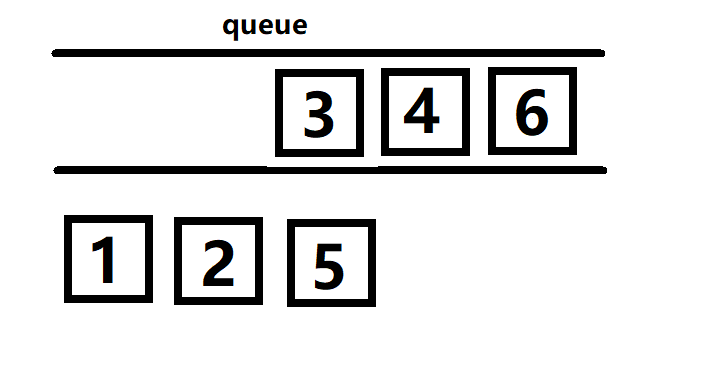
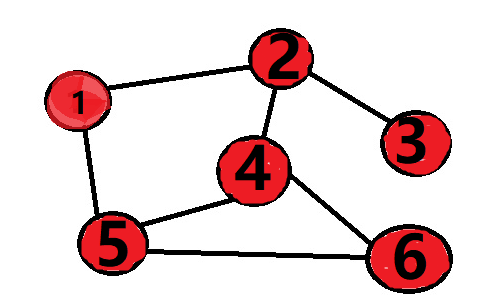
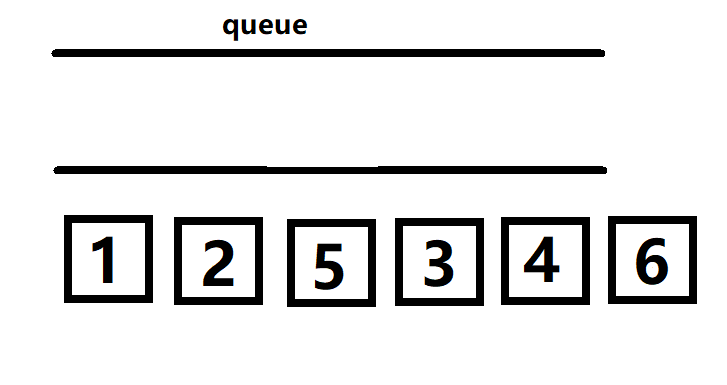
最后把队列中的3 4 6 拿出来,由于没有点可以再放入到队列中所以就得到了结果 :1 2 5 3 4 6
大概思想我们讲完了,作者比较菜,大家有什么不懂可以参考B站大佬正月点灯笼的视频附上链接https://www.bilibili.com/video/av25761720
讲完思想我们来做题,hdu的1548和 2717 以1548为例子
A strange lift
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 38453 Accepted Submission(s): 13524
Problem Description
There is a strange lift.The lift can stop can at every floor as you want, and there is a number Ki(0 <= Ki <= N) on every floor.The lift have just two buttons: up and down.When you at floor i,if you press the button “UP” , you will go up Ki floor,i.e,you will go to the i+Ki th floor,as the same, if you press the button “DOWN” , you will go down Ki floor,i.e,you will go to the i-Ki th floor. Of course, the lift can’t go up high than N,and can’t go down lower than 1. For example, there is a buliding with 5 floors, and k1 = 3, k2 = 3,k3 = 1,k4 = 2, k5 = 5.Begining from the 1 st floor,you can press the button “UP”, and you’ll go up to the 4 th floor,and if you press the button “DOWN”, the lift can’t do it, because it can’t go down to the -2 th floor,as you know ,the -2 th floor isn’t exist. Here comes the problem: when you are on floor A,and you want to go to floor B,how many times at least he has to press the button “UP” or “DOWN”?
Input
The input consists of several test cases.,Each test case contains two lines. The first line contains three integers N ,A,B( 1 <= N,A,B <= 200) which describe above,The second line consist N integers k1,k2,….kn. A single 0 indicate the end of the input.
Output
For each case of the input output a interger, the least times you have to press the button when you on floor A,and you want to go to floor B.If you can’t reach floor B,printf “-1”.
Sample Input
5 1 5
3 3 1 2 5
0
Sample Output
3
思路:每次乘坐电梯有向上和向下两种情况,所以我们就分别看这两种情况是否会超出楼层范围,如果没有超出范围我们就加到队列里面,然后继续拿队首的元素进行搜索看是否到达了终点楼层,如果到了就返回次数,如果队列都空了还没有到终点那么就无法到达,返回-1。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e4;
int n,s,b;
int k[maxn],vis[maxn];
struct node{
int step,h;
};
bool check(node p)
{
if(p.h<=0||p.h>n||vis[p.h]) //检查是否越界或者已经访问过
return false;
return true;
}
int bfs()
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); //对每组数据的vis初始化
node a,next;
queue<node> q;
a.step=0;
a.h=s;
q.push(a);
vis[a.h]=1;
while(!q.empty())
{
a=q.front();
q.pop();
// cout<<"a.h="<<a.h<<" "<<a.step<<endl;
if(a.h==b) return a.step;
next=a;
next.h=a.h+k[a.h]; //向上乘坐电梯
if(check(next))
{
next.step=a.step+1; //如果符合条件就加一次 然后继续放到队列中
q.push(next);
vis[next.h]=1;
}
next.h=a.h-k[a.h]; //向下乘坐电梯
if(check(next))
{
next.step=a.step+1;
q.push(next);
vis[next.h]=1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
while(cin>>n)
{
if(n==0) break;
cin>>s>>b;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>k[i];
cout<<bfs()<<endl;
}
return 0;
}

|

|
